Posted by Horton Tatarian, research biochemist, on 12th Mar 2016
Anti-Inflammatory Diets

Diet and Disease
Two problems cause the epidemic, chronic diseases:
- Chronic inflammation
- Failures in the repair of body tissues
So, the best diet for human health will do two things for you:
- Reduce inflammation in your body
- Promote the repair of your body tissues
Please remember:
The failure of tissue repair is the direct cause of all chronic diseases. The right foods and dietary supplements have top priority in fueling the repair of your body tissues.
The bulk of your diet should consist of a wide variety of whole, minimally processed, plant-based foods.
Scientific studies on human diets compare eating habits with patterns of disease. The diseases of industrialized nations correlate with the consumption of prepackaged commercial foods and fast-foods. The following screenshot of subtopics on the notoriously unhealthy Western diet lists most of the characteristics of harmful foods.
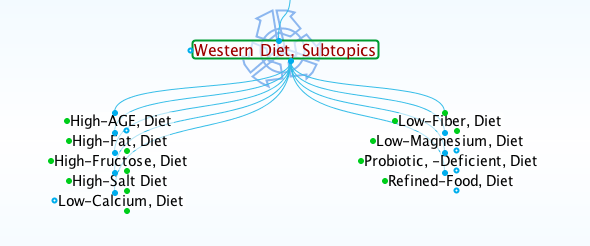
Life Sciences Database Screenshot, Western Diet Subtopics, Lifesciences.care
AGE in "High-AGE Diet" refers to Advanced Glycation End-Product, a scientific term for a group of highly destructive chemicals formed by high-heat cooking. AGEs form in foods when fried, broiled, baked, roasted, grilled, or toasted but not when boiled or steamed.
Each subtopic of the Western diet links to some research articles. For example, the following excerpt is from a report indexed to Low-Fiber Diet.
Colonic diverticulosis is the most frequent structural abnormality of the large bowel, although it was a rarity before the 20th century. Lifestyle changes in westernized societies with reduced fiber diet are supposed to be the main cause for its high prevalence nowadays. In African countries, where staple diet is rich in fiber, diverticulosis remains very infrequent. Reference
Diabetes type 2, cancer, and other disease topics also link to low-fiber diet. However, for most chronic diseases, scientific data highlight insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables in disease susceptibility or causation.
From a scientific point of view, national campaigns to increase vegetable and fruit consumption are justified . . . to decrease the burden of several chronic diseases in Western societies. Reference
The nutritional value of fruits and vegetables make them preferred sources of dietary fiber as compared to whole grains. The sprouting of seeds and grains converts them into tender vegetables (sprouts) with far greater nutritional value than in their original state.
Diet and Inflammation
Low-grade inflammation is a primary link between poor diet and disease. This relationship is similar to that between physical inactivity and disease. One benefit of regular activity is a lowering of low-grade inflammation, a problem usually detected by blood tests. Scientists discuss the protective, anti-inflammatory effect of exercise.
The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise . . . may contribute to mediate the beneficial health effects of exercise training in patients with chronic diseases associated with chronic low-grade inflammation. Reference
Likewise, healthful diets are protective, anti-inflammatory, and described by research findings within the following subtopics of Healthful Diet.
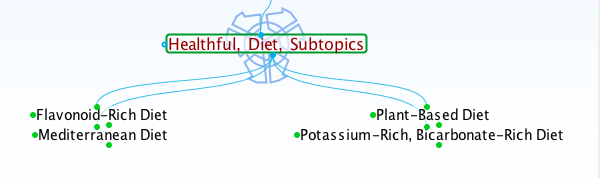
Life Sciences Database Screenshot, Healthful Diet Subtopics, Lifesciences.care
Diets including plenty of fruits and vegetables are rich in flavonoids, potassium, and bicarbonate, substances that reduce or prevent inflammation. The Mediterranean Diet includes foods typical of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. This diet is plant-based and contains some olive oil. All healthful diets supply natural, whole foods traditionally free of pesticides and herbicides.
Adherence to the traditional Mediterranean diet was associated with a reduction in the concentrations of inflammation and coagulation markers. This may partly explain the beneficial actions of this diet on the cardiovascular system. Reference
On the contrary, Western diets promote tissue destruction through low-grade, chronic inflammation. Findings on the characteristics of favorite Western foods point to a series of dietary-caused metabolic stresses. In effect, the Western diet is a potent recipe for chronic disease. The weaknesses of Western diets appear in the following screenshot of associated topics.
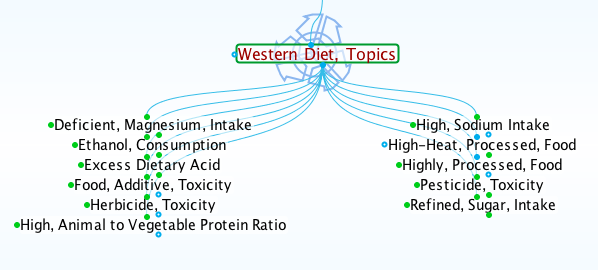
Life Sciences Database Screenshot, Western Diet Topics, Lifesciences.care
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Anti-inflammatory diets work in two ways. These diets:
- Omit foods, drinks, and food products that contain inflammatory chemicals, whether synthetic or natural
- Include foods and other plant substances that innately provide anti-inflammatory effects
In addition to natural, whole, chemical-free foods, most anti-inflammatory diets include herbs and spices. Beneficial spices include cardamom seed, cayenne, celery seed, cinnamon, fennel seed, garlic, ginger, marjoram, nutmeg, and turmeric.
For example, scientific research on turmeric, an ingredient of Indian curry, identifies curcumin as the most active anti-inflammatory component. The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin is responsible for scientific reports of benefits in a broad range of disease states.
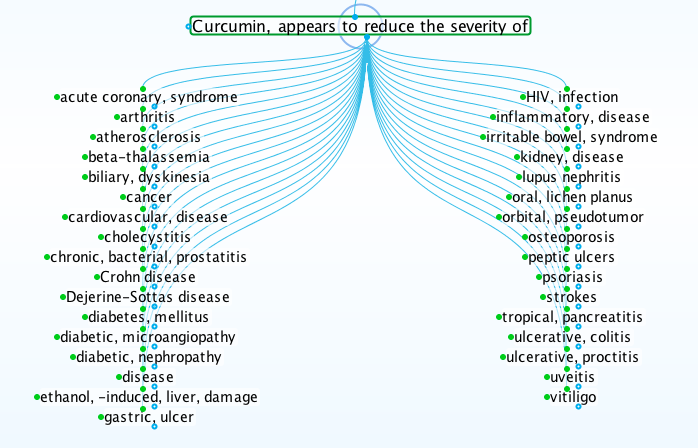
Life Sciences Database Screenshot, Curcumin appears to reduce the severity of, Lifesciences.care
However, as with many other natural anti-inflammatory substances, curcumin does not actually treat any particular disease. Instead, its natural regulatory effect reduces inflammatory processes common to many diseases.
In other words, curcumin modulates the biochemistry of inflammation, some of the major pathways involved in the development of inflammatory disorders. Inflammatory disorders include most chronic diseases.
Regular exercise and anti-inflammatory diets promote health in the same way.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Guidelines
An analysis of scientific data at Life Sciences LLC supports the following recommendation.
- Increase your intake of pure water and wholesome foods and beverages as quickly as you find comfortable. Take your time; let your body adjust to changes, but do not procrastinate attending to your needs.
- Take appropriate dietary supplements consistently six days per week. Take only recommended exceptions on the 7th day. This pattern allows “resets” to cell metabolism and provides a welcomed break from the routine.
- Avoid all foods to which you may be allergic or sensitive. Be aware that prescription drugs may interact with nutrients in foods or dietary supplements. Consult your physician, pharmacist, or drugs.com. Otherwise, nutritious foods and beverages include but are not necessarily limited to:
- Vegetables, raw and steamed, in all types and colors such as greens, carrots, yams, squash, and beets
- Fruits, fresh and frozen: berries, cherries, apples, peaches, apricots, pomegranate, and others
- Whole grains and legumes: quinoa, millet, buckwheat, lentils, steel-cut oats
- Nuts, seeds, nut/seed butter, in limited amounts. Examples: raw walnuts, pecans, cashews, and sesame seed
- Organic eggs, limited to one or two eggs only two or three days per week
- Wild Alaskan fish and sardines, in limited amounts one or two days per week
- Extra virgin olive and coconut oils, limited to 1 – 2 tablespoons daily onto salads and vegetables
- Herb seasonings. For example, basil, cilantro, parsley, rosemary
- Spice seasonings. For example, cayenne, cinnamon, fennel seed, garlic, ginger, marjoram, nutmeg, and turmeric
- Herb teas (especially green tea), fresh vegetable juices with fiber included, and pure water
Do not consume sodas, alcoholic beverages, sugar, artificial sweeteners, or foods and drinks containing sugar, artificial sweetener, and synthetic ingredients. Avoid fruit juices; eat the fruit instead.
Strictly minimize or eliminate meats, particularly beef. Also avoid Atlantic fish and large fish apart from wild Alaskan varieties.
Avoid commercial pasteurized and homogenized dairy products. Strictly minimize raw milk and cheese. However, high-quality colostrum and whey may be beneficial.
Avoid consuming most commercial rice, corn, wheat and baked goods prepared from rice, corn, and wheat. These grains contain high levels of toxic pollutants. Baking creates additional toxins.
Healthful foods become inflammatory through chemical changes caused by exposure to high heat. Do not consume broiled, baked, roasted, fried, or toasted, or browned foods as a routine. Maximum safe cooking temperatures are those reached by boiling and steaming. Higher temperatures create highly toxic aldehydes (AGEs) within the food.
Related Articles:
Next: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Supplements
About Horton Tatarian

I’m a biochemist who examines scientific findings on health and disease. My degree in biochemistry is from U.C. Berkeley. UCLA School of Medicine granted an M.D. degree in 1974. Since then, independent research prepared me to advise clients on natural ways of self-care.

